smartWiFi
|
What not leverage modern IoT tools to command and control a fischertechnik model?
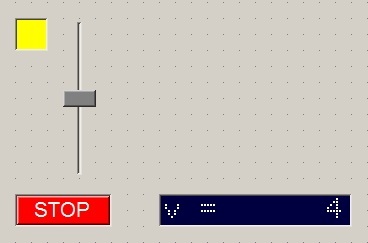
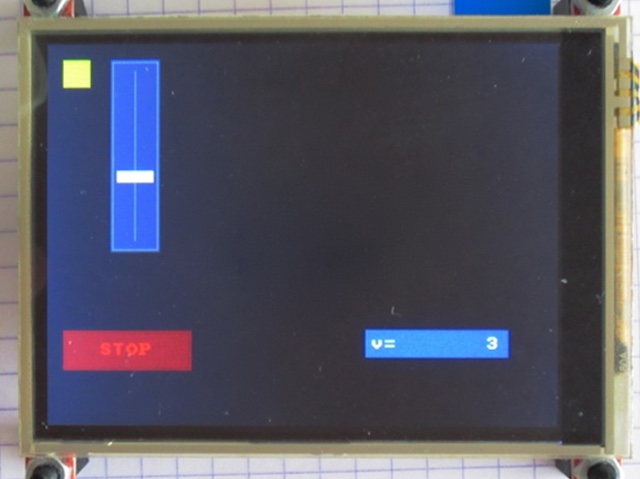
This project is shared with the Embedded Computing website, as the whole development is carried out with the tools I use for embedded computing. This part in more functional oriented. The Internet of Things brings a new generation of command and control dashboards, operated remotely and featuring a nice interface and design. How to turn the standard panel on the right into something more appealing? |
|
Functional Description
|
Compared to the RoboTX controller, one of the major feature the Robotics TXT controller brings is the WiFi interface. The idea of the smartWiFi device is to provide a WiFi connectivity to the RoboTX controller.
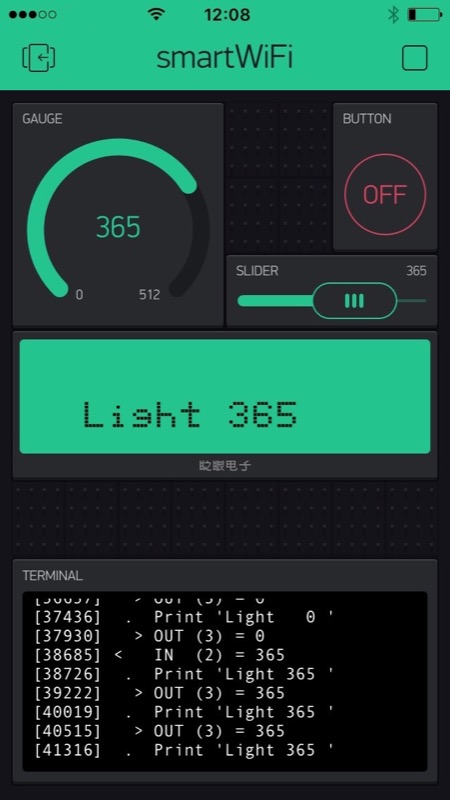
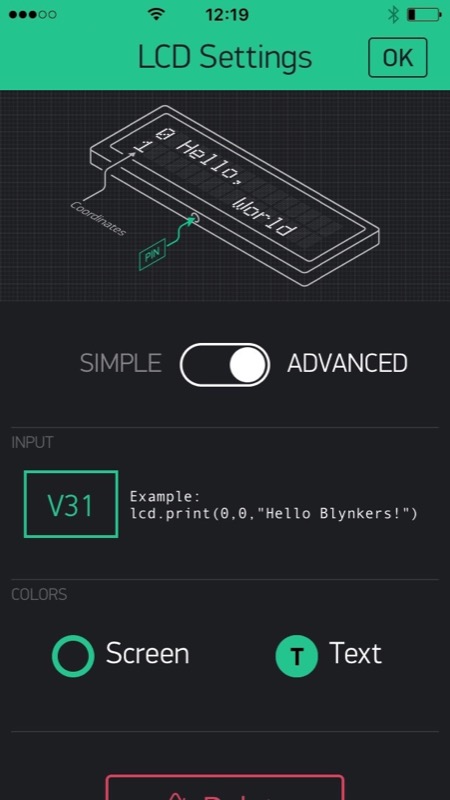
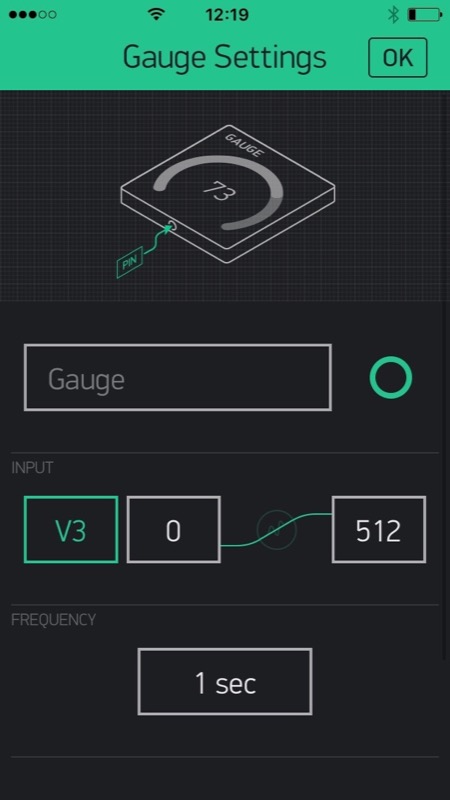
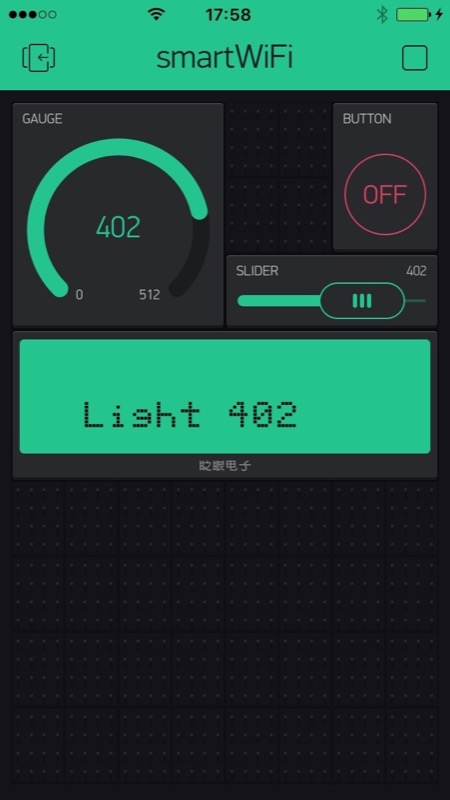
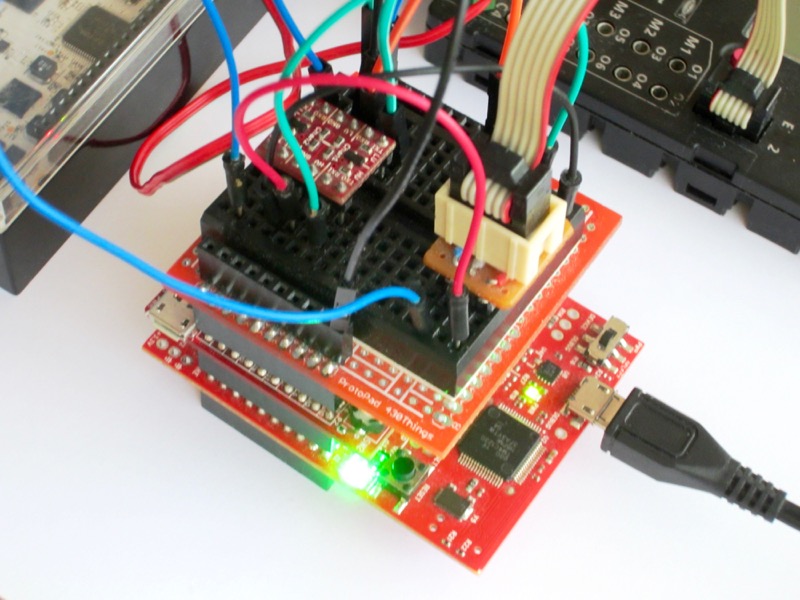
The features include sending data and text, and receiving data and commands. Data, text and commands leverage the Blynk service and the apps for iOS and Android, which provide a nice GUI to the end-user. The device should be compact enough to fit inside the red power block (reference 30263) case, be connected through I²C, and feature low consumption to be powered by the RoboTX controller. The commands should be easy to deal with, with a ready-to-use driver for Robo Pro. |
User Interface
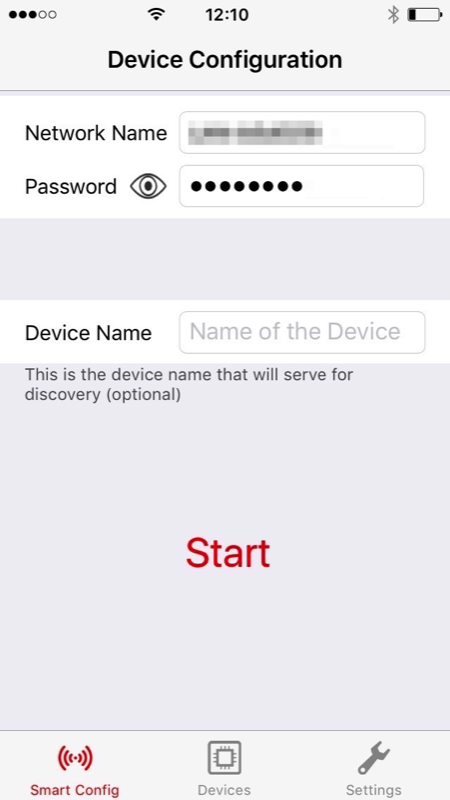
WiFi Provisioning
|
Modern WiFi devices features automatic provisioning, like the SmartConfig for the CC3100 and CC3200 WiFi radios.
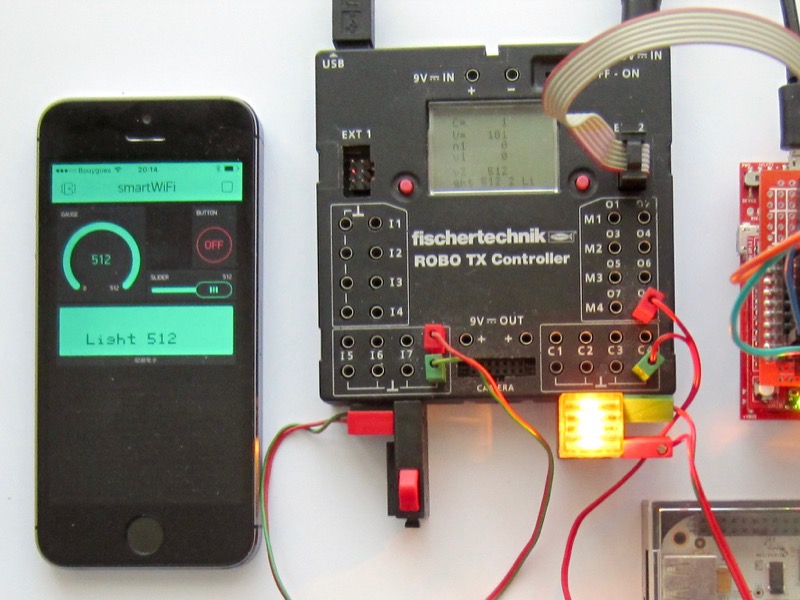
For the first connection, an Android or iOS app looks for the WiFi radio, configures the device automatically and saves that configuration. Subsequent connections use the previously saved configuration. Then the smartWiFi device connects to the server. On the other end, once the smartphone is also connected to the same server, data and commands go to and fro between the RoboTX and the smartphone. |
Interface Commands
|
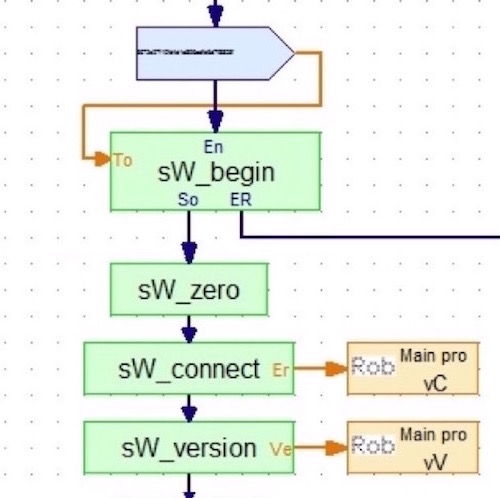
There are two sets of commands.
|
|
The first set of commands initialises and manages the connection to the server.
|
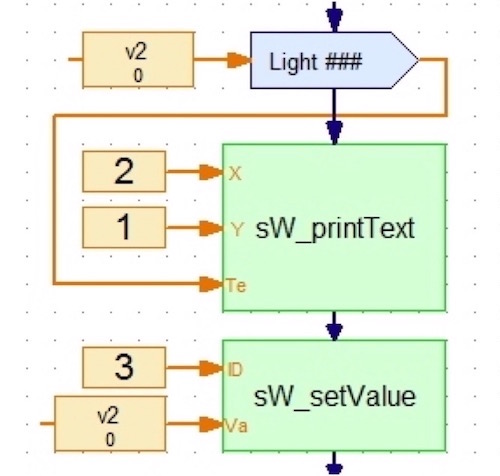
The second set of commands sends and receives values, prints text on the screen and provides utilities.
|
|
Find more details about the I²C driver at the I²C Remote WiFi Interface smartWiFi page.
|
Working Prototype
Finalised and Working Device
|
The device in encased in the standard 9 x 3 cm red box with the I²C ribbon cable connected to the RobotTX.
A separate cable provides the power line. There is a variant based on Bluetooth Low Energy called smartBLE. |