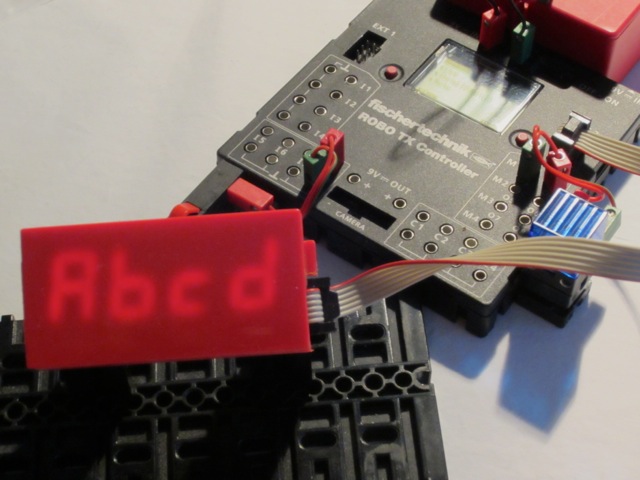
smartLED
Commands
|
The command begin initialises the display and the command clear switches all segments off.
The value sent to the display can be decimal —range 0000~9999— or hexadecimal —range 0x0000~0xffff. A decimal point can be defined and leading zeroes omitted. 00.12 is displayed as 0.12, with the first zero omitted. A specific command defines the segments to light on for a given digit, based on the binary coding of the segments:
For example,
The I²C 4-Digit 7-Segment LED DIsplay smartLED page provides more details about the commands and the RoboPro visual interface. |