How to Connect an I²C Device to the Robotics TXT?
|
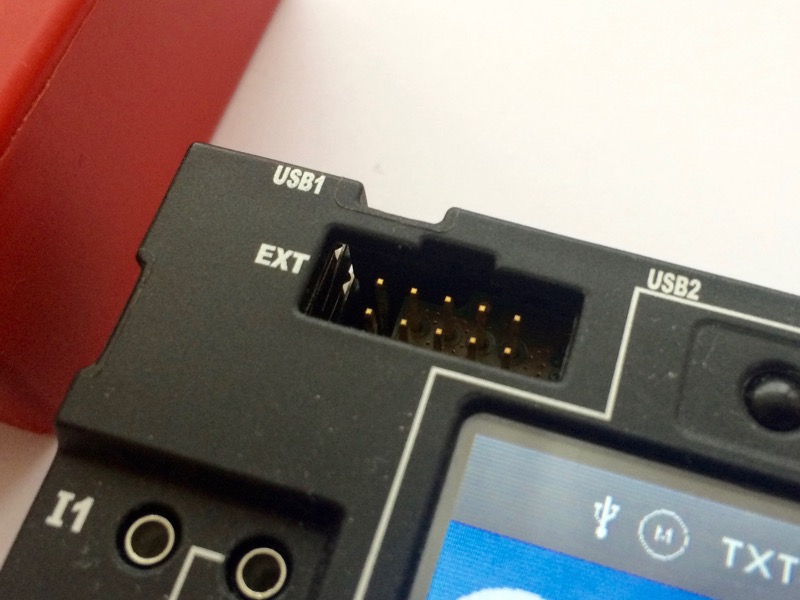
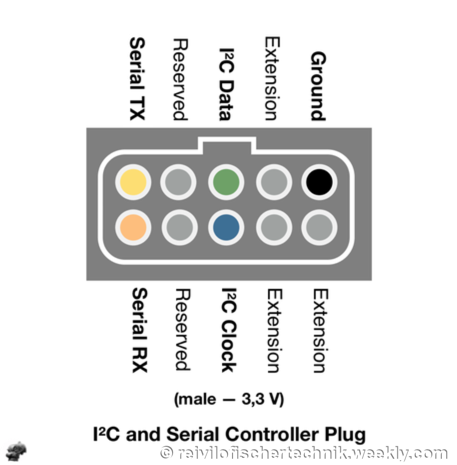
fischertechnik Robotics TXT controller has one extension port, EXT. This port operates at 3.3 V level.
The extension port EXT supports I²C connection, with 3 active wires:
|
Contrary to what has been posted in the ft:c forum, video and even issue 2015-4 of ft-pedia, pin 9 of the extension port does not provide +3.3V power supply. |
|
I²C only defines a bus protocol, nothing more.
|
|
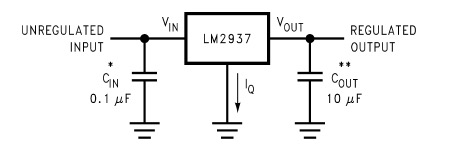
How to power the sensor with 3.3 V?
There's no special difficulty in assembling a separate 3.3 V power line with a LM2937-3.3 or LM1117-3.3, or similar based on the estimated power consumption of the devices. The unregulated input is connected to the +9V output of the Robotics TXT, and so does Ground to Ground. |
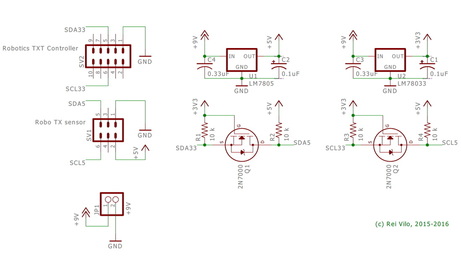
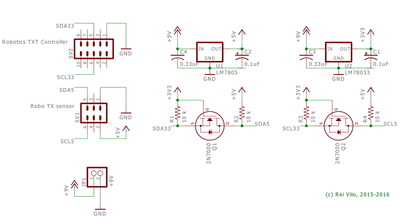
Connecting 5 V I²C Devices to Robotics TXT Controller
|
Some of the I²C devices I've developed libraries for, like the AMIS-30624 stepper controller or the 4 lines x 20 characters LCD display, run at 5 V.
The circuit requires dual regulators for 3.3 V and 5 V power lines, and MOSFETs or PCA9306 to step-up I²C signals from 3.3 V to 5 V. Please refer to the different I²C Logic Level Converter options and the official Level shifting techniques in I2C-bus design application note from NXP. Some voltage regulators require a minimum power usage to ensure good stability. In such a case, just place a LED with a limiting resistor on the 3.3 V power rail. The two circuits on the right combine the solutions mentioned above. • Caution |
Compatibility Issues
|
The I²C implementation in RoboPRO 4.2.4 for the Robotics TXT controller suffers from three limitations:
Luckily, the RoboTX controller fully supports I²C fast mode (400 kHz). |
|
I do not recommend the logic level converter for I²C described in issue 2016-4 of ft-pedia, as it doesn't match with the Level shifting techniques in I2C-bus design application note from NXP.
|
The circuit proposed on issue 2016-4 of ft-pedia doesn't match with the Level shifting techniques in I2C-bus design application note from NXP. |